Introduction
In the realm of athletic performance, the quest for optimal nutrition is a journey that often leads athletes to explore the profound impact of micronutrients on their capabilities. Among these, Vitamin B12, an essential water-soluble vitamin, has emerged as a key player in the intricate tapestry of athletic potential. As athletes continually seek ways to enhance their endurance, strength, and overall performance, understanding the relationship between Vitamin B12 and exercise becomes paramount.
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, plays a pivotal role in various physiological processes crucial for athletic success. Its primary functions include the formation of red blood cells, DNA synthesis, and the maintenance of the nervous system. Unlike some other vitamins, the human body cannot produce Vitamin B12, making it imperative to obtain an adequate supply through diet or supplementation.
Athletes, with their heightened physical demands, rely on an efficient metabolism and optimal oxygen-carrying capacity for peak performance. Vitamin B12 contributes significantly to these aspects, making it a nutrient of special interest for those engaged in rigorous training and competition.
Dietary sources of Vitamin B12 predominantly include animal products such as meat, fish, and dairy. However, for athletes adhering to specific dietary preferences or facing absorption challenges, achieving sufficient Vitamin B12 intake may require careful consideration and planning.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency and its Impact on Athletes
While the importance of Vitamin B12 in supporting exercise performance is clear, it is equally crucial to understand the consequences of deficiency, particularly in the context of athletic endeavors. Athletes may be at an increased risk of Vitamin B12 deficiency due to factors such as rigorous training, specific dietary choices, or medical conditions affecting absorption.
Common Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Athletes experiencing a deficiency in Vitamin B12 may encounter a range of symptoms that can detrimentally affect their training and competition. These symptoms include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, and impaired concentration—factors that can significantly hinder overall athletic performance.
Moreover, the impact of Vitamin B12 deficiency extends beyond physical symptoms to encompass neurological manifestations. Athletes may experience tingling or numbness in extremities, difficulties with balance and coordination, and cognitive issues. These neurological symptoms emphasize the intricate link between Vitamin B12 and the optimal functioning of the nervous system, crucial for precise and coordinated movements in sports.
Implications for Exercise Performance: The consequences of Vitamin B12 deficiency on exercise performance are far-reaching. Inadequate levels of this vitamin can compromise an athlete's ability to sustain energy levels, impede optimal oxygen transport to muscles, and hinder the recovery processes essential for continuous training adaptations.
Athletes with undetected or untreated Vitamin B12 deficiency may find themselves facing a plateau in performance, increased susceptibility to injuries, and a longer recovery time after intense training sessions. Therefore, regular monitoring of Vitamin B12 levels and prompt intervention in the case of deficiency are vital components of an athlete's overall health and performance management.
Nutritional Strategies for Athletes
As athletes strive for peak performance, integrating Vitamin B12 into their nutritional strategies becomes a key component of success. Here are practical and effective ways for athletes to ensure they meet their Vitamin B12 requirements:
-
Diversify Your Diet:
- Incorporate a variety of Vitamin B12-rich foods into your diet. Animal products such as lean meats, fish, eggs, and dairy are excellent sources.
- For those following vegetarian or vegan diets, explore fortified plant-based alternatives like fortified cereals, plant-based milk, and nutritional yeast.
-
Lean Meat and Fish Choices:
- Opt for lean cuts of meat and fish to obtain Vitamin B12 without excessive saturated fats. Fish such as salmon, trout, and tuna are not only rich in B12 but also provide omega-3 fatty acids, beneficial for cardiovascular health.
-
Dairy Delights:
- Include dairy products like yogurt and cheese in your diet. These not only contribute to Vitamin B12 intake but also provide essential nutrients like calcium and protein.
-
Eggs for a Nutrient Boost:
- Eggs are not only a versatile and protein-rich food but also an excellent source of Vitamin B12. Include them in various forms in your diet, such as scrambled, boiled, or as part of dishes like omelets.
-
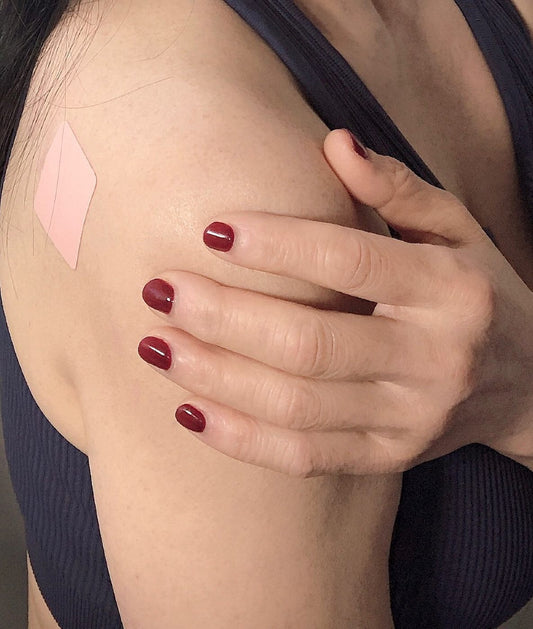
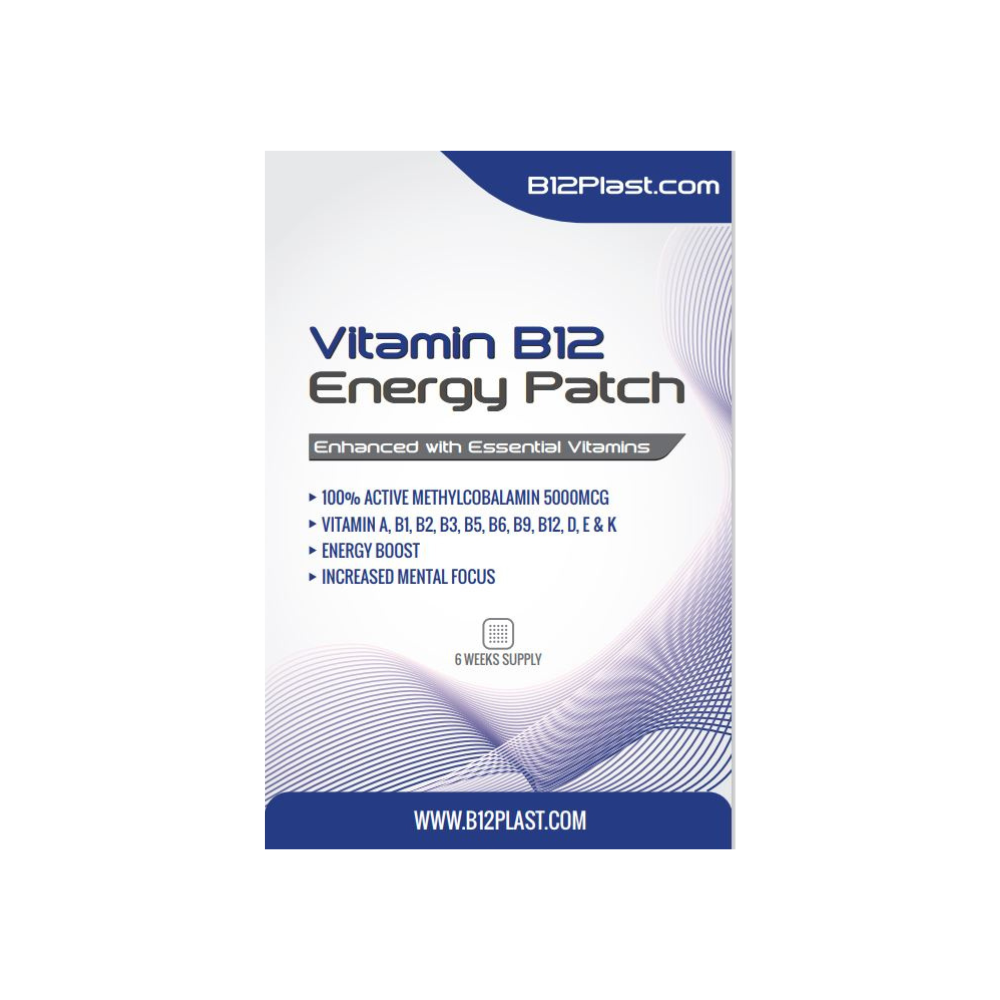
Supplementation Considerations:
- Athletes facing challenges in meeting their Vitamin B12 requirements through food alone may consider supplementation.
- Consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to determine the appropriate dosage and form of Vitamin B12 supplements, as individual needs can vary.
-
Meal Timing and Consistency:
- Ensure a steady intake of Vitamin B12 by spreading it throughout the day. Consistent and balanced meals contribute to stable nutrient levels, supporting sustained energy during training and recovery.
-
Hydration Habits:
- Stay adequately hydrated, as proper hydration supports nutrient absorption. Water is essential for various physiological processes, including the absorption and utilization of vitamins.
-
Collaborate with Nutrition Professionals:
- Seek guidance from nutritionists, dietitians, or sports nutrition specialists who can provide personalized advice based on your training regimen, dietary preferences, and health status.
Conclusion
As athletes navigate the intricate relationship between Vitamin B12 and exercise performance, it is crucial to recognize that optimal results stem from a holistic approach. Balancing nutrient intake, incorporating lifestyle considerations, and staying attuned to individual needs collectively contribute to unlocking athletic potential.
Empowered with knowledge, athletes can make informed decisions regarding their nutrition, supplementation, and overall well-being. By embracing a comprehensive approach that encompasses diet, lifestyle, and a commitment to continuous improvement, athletes can enhance their performance, support long-term health, and embark on a journey towards sustained excellence.
In your pursuit of athletic greatness, let this holistic approach be your guide, propelling you towards new heights of achievement and well-being.